|
|
|
Your search within this document for 'konsepto,number' resulted in 21 matching pages.
|
| 1 |
 |
“...given me as guide.
Data about the vernacular names and the medicinal use of plants
were chiefly furnished by Messrs. G. R. van Dussel, Dr. P. de
Haseth Möller, F. J. C. Beaujon, J. L. J. C. Cadières, de Wind,
A. Hermus, H. J. Cohen Henriquez, Th. van Sadelhoff and P. A.
Euwens. Mr. Duyfjes gave me much informations about the geology
of the islands.
In the elaboration of the collected plants I was helped by Prof.
I. Urban who gave a number of indications for forms not directly
known to me, while Dr. F. Niedenzu, Dr. L. Radlkofer and Mr. 0.
E. Schulz named a number of the Malpighiaceae, Sapindaceae and
Solanaceae. Dr. H. Hallier determined by far the greater part of
the Convolvulaceae. Prof. W. Trelease determined the Agave
species and Dr. A. S. Hitchcock some Gramineae.
To the Director of the State Herbarium at Leyden I am indebted
for the loan of the plants of the Suringar collection.
I have particularly to thank Prof. N. L. Britton who sent me the plants
collected by himself in Curasao to...”
|
|
| 2 |
 |
“...X
Preface.
an extensive correspondence on forms that were difficult to deter-
mine. Thanks to his communications and assistance with the
determinations a number of plants have now been named with
greater certainty, than would have been possible without his
valuable help which was especially necessary with the Cactaceae.
This Flora is divided in Three Parts; whereas the different Parts,
Sections and Chapters need no further explanation, a short account
of the methods I followed in nomenclature, synonymy and distri-
bution of plants is given here.
The enumeration of Families and Genera is very nearly given
after the order of De Dalle Torre et Harms: Genera siphonoga-
marum ad systema Englerianum Conscripta (1908).
In a few cases I thougt it better to follow:
Urban: Symbolae Antillanae and Urban: Additamenta ad Cog-
nitionem Florae Indiae Occidentalis 1892—97.
The names of the species used are mostly drawn from these two
papers and Engler und Prantl.: Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien
up to...”
|
|
| 3 |
 |
“...115
cinal use of many plants in Simon’s bookx) which also gives an
extensive list of vernacular and Latin plant names, composed by
Dr. N. Anslyn, military physician. That in such a list many inac-
curacies in the determinations occur is obvious.
I also became aequainted with a publication by Hurtado1 2),
who in an appendix gives a survey of the Curasao flora. This
appendix contains a very large number of mistakes.
It seemed preferable not to quote the plants from the three
publications mentioned and to elaborate in this flora only the
data from recent collections, found in the Utrecht herbary.
1) G. J. Simons. Beschrijving van het eiland Curapao. Oosterwolde 1868.
2) 0. Hurtado. Compendlo di botanica elemental. Curazao. Benthencourt e
Hyos. 1891....”
|
|
| 4 |
 |
“...of the Botanical Laboratory of het University
at Utrecht is a fairly large collection of plants, gathered in Curasao
by Aschenberg. I have not succeeded is obtaining nearer infor-
mation about it. It will be seen from the Systematical part of
this Flora that a great many of the species, found by Suringar
and myself, have also been collected by Aschenberg.
Collection F. A. F. C. Went.
A number of plants has been collected by Prof. Dr. F. A. F.
C. Went during his stay in Curasao in 1901. In the Systematical
list they are indicated by the name Went.
Collection Miss A. Lens.
In 1907 Miss Lens collected a number of plants in Curasao;
this small collection is conspicuous by its fine specimens, since
Miss Lens could take much time in drying them. They are chiefly
ruderal plants and mentioned in the list by the name Lens,
Collection W. Versluys.
In 1907 Mr. W. Versluys, Government Agriculturalist made
a collection of plants, indicated in the list as Yersluys. It con-
tains especially grasses.
Collection...”
|
|
| 5 |
 |
“...Museum, in the Martius Herbary at Brussels and in the Wildenow
Herbary at Berlin a number of plants from Curasao are found.
F. Bredemeyer (1758—1839) visited CuraQao about 1787, his col-
lections are in the K. K. Hofmuseum at Vienna and in the her-
bary of the Botanical Museum at Berlin.
J. Read also collected in Curasao; his collections are in the
Academy of Nat: Science at Philadelphia; West-Indian plants
also in the Krug und Urban Herbary at Berlin.
H. F. A. Baron von Eggers visited CuraQao in 1893; it is not
known to the present author whether he also collected plants there.
It did not seem advisable to spend time on a search for these
plants, since in all probability this would not result in any new
information. _ (< . '
From N. J. Jacquin, Selectarum stirpium Americanarum historia
(1763), appears that at that time some sixteen plants from CuraQao
were already known, while also in Linn. Spec. (1753) a number
of data about CuraQao plants are spread....”
|
|
| 6 |
 |
“...places (Boeroe-
koe 21 M.) reminds one of the limestone hills on the South coast
of Curagao. The Canashito is a more inwardly situated limestone
ridge. From the plain of West Aruba rises isolated the conical
Hooiberg, 164 M. Also the Seroe Plat, 94 M., is an isolated moun-
tain and is surmounted by a caleareous table-land.
The diabase hilly complex, extending over a territory, bordered
by lines from Matavidiri to Belashi, from there to Boca Prins
and then along the North coast to Matavidiri, has a number of
high tops, among them Ariekok 175 M. and Jananota 188 M.
From these tops the country slowly descends to the South and
West and the whole landscape is dominated by cup-shaped hills,
separated by gently sloping valleys; in some places we find per-
pendicular walls. On the North coast we meet in a few places
the same limestone terraces which exist on the West coast of
Curagao.
Bonaire.
The West point of the island lies at ± 68° 12' W. Long, and
12° 14' N. Lat., the most Southern point at ± 68°...”
|
|
| 7 |
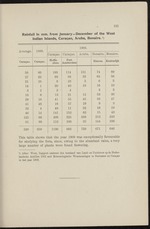 |
“...Bonaire. Bonaire.
Curasao. Curasao. Hoffle abau. Fort Amsterdam Rincon. Kralendijk
58 60 193 114 131 74 89
27 22 93 93 33 64 56
21 28 8 10 2 6 5
14 1 30 40 19 16 10
3 2 2 4 3 3
18 9 13 21 12 53 30
29 18 41 55 45 58 47
41 46 16 57 19 9 3
33 4 48 11 52 16 19
46 14 141 153 63 15 43
125 66 498 325 358 213 233
81 89 113 100 25 144 108
526 359 1196 983 759 671 646
This table shows that the year 1909 was exceptionally favourable
for studying the flora, since, owing to the abundant rains, a very
large number of plants were found flowering.
1) After: Went, Rapport omtrent den toestand van Land- en Tuinbouw op de Neder-
landsehe Antillen 1902 and Meteorologische Waarnemingen in Suriname en Curasao
in het jaar 1909....”
|
|
| 8 |
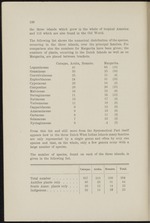 |
“...e 11 15 (12)
Rubiaceae 13 17 (4)
Verbenaceae 11 19 (0)
Capparidaceae 9 12 (9).
Amarantaceae 9 13 (6)
Cactaceae 8 11 (3)
Solanaceae 7 23 (2)
Nyctaginaceae 6 ,4 (3)
From this list and still more from the Systematical Part itself
appears how in the three Dutch West Indian Islands many families
are only represented by a single genus and often by only one
species and that, on the whole, only a few genera occur with a
large number of species.
The number of species, found on each of the three islands, is
given in the following list.
Curasao. Aruba. Bonaire. Total.
Total number 357 213 239 394
Antilles plants only 40 25 31 44
South Amer. plants only . . . 20 12 14 22
Indigenous 22 14 18 25'...”
|
|
| 9 |
 |
“...139
Hence the ratios of total number of the three groups are approxi-
mately as 360: 220: 250. The present author knows no reason why
this should be so; probably there is no connection with the ratio
of the surfaces of the islands which is as ± 360:119:153.
Taking into consideration all the wild plants, except those which
are also found in the Old World and in North and South America,
the three Dutch Islands share 106 plants or 25% more with.
South than North America and 42 plants or 10% more with
Central than North America. . . . ..
Comparing these numbers with the corresponding ones for the
flora of Portorico!), where they are 15 % and 7 %, we see that
the Dutch West Indian Islands contain relatively more Central
and South American plants than Portorico, although this island
has already a fairly large number of South American plants.
What Urban says (p. 681): „dass die Flora von Portorico die
st&rksten Beziehungen zu Siid-Amerika aufweist”, holds still more
for Curasao, Aruba and Bonaire...”
|
|
| 10 |
 |
“....
Curasao.
Curagao. Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Curagao. Aruba. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Curagao. Aruba? Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Bonaire.
Curagao. Aruba. Bonaire.
Only a smal number of these plants give a typical aspect to the vege-
tation and occur so abundantly that they are an important factor
in imparting to the flora of these islands a character of its own.
See on this, point Third Part, Section C.
10...”
|
|
| 11 |
 |
“...to be
expected. The type of vegetation on the Leeward Islands might
be generally described as a Croton vegetation, here as on the
Windward Islands determined by plants like Croton, Acacia,
Lantana, Melochia, Opuntia, Melocactus, to which for the Leeward
Islands may be added a number of other plants, as will appear
from the further description. On the Leeward still more than on
the Windward Islands this type of vegetation cannot be distinctly
separated from the litoral vegetation which only near the salt-pans
assumes a character of its own by the occurence of Mangrove
plants.
In many parts of the Islands culture or traces of former culture
are found; also ruderal plants are found everywhere, among which
a large number of tropical cosmopolitans. A genuine original
vegetation is only found in" the higher parts.
We saw that in general there is some difference in the vegetation,
depending on shrubs or herbs being more prominent; a division
according to the occurrence or non-occurrence on calcareous...”
|
|
| 12 |
 |
“...Aruba and Bonaire.
If only a small number of plants is available to settle a vegetation
type it will be seen on comparison with the list of the plants
that’are only found in the Dutch W.I. Leeward Islands, that among
the plants, typical for this purpose, not a single indigenous one
occurs. Hence the aspect of the vegetation in the three Islands is riot
typically individual by the occurrence of definite indigenous plants
but depends on plants that also occur elsewhere.
Now leaving aside certain types of the vegetation and looking
at it as a whole, we are particularly struck by the Cereus species
which ar either indigenous or South American, the Melocacti,
which are indigenous and other indigenous plants that predo-
minate in certain parts,' the Agaves, Phyllanthus Euwensu,
Peltophorum Suringari, Chloris leptantha, Eragrostis Urbamana.
Beside this small number of indigenous plants of which the
Cactaceae may be said to occur everywhere, we have a large number
of Antilles plants, as: CoCcoloba...”
|
|
| 13 |
 |
“...152
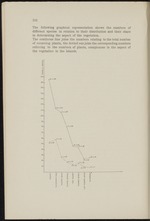
The following graphical representation shows the numbers of
different species in relation to their distribution and their share
in determining the aspect of the vegetation.
The continous line joins the numbers relating to the total number
of occurring plants, the dotted one joins the corresponding numbers
referring to the numbers of plants, conspicuous in the aspect of
the vegetation in the Islands.
170. _
140..
110. _
C = 106
100..
D = 80
G =22
h = 7
m...”
|
|
| 14 |
 |
“...153
Hence:
A : a = 3,1
C : c = 4,1
D : d = 5
E : e = 3,7
G : g = 2,4
These equations show as well as the general shape of the curves
that: '.
if we compare the total number of plants with the number ot
those that determine the vegetation, this latter number is relatively
smaller with the South American plants than with the indigenous
Antilles plants, smaller again with these than with the plants
growing in the Antilles and for these again smaller than with
the indigenous South American plants.
So we conclude that the influence of the South American flora is
strongest; we saw (p. 139) that also numerically this influence
is stronger on the flora of the Dutch W. I. Islands than on that
of Portorico.
Still I should conclude from what I have personally seen and
from the tables about the distribution of the Antilles plants and
of the purely South American ones, that the outward appearance
of the vegetation, in spite of the typical Cereus. species which
are either indigenous or South American...”
|
|
| 15 |
 |
“...the three Islands no
sharp demarcation lines can he drawn between the various
types of vegetation. For this reason I shall not give an enume-
ration of the plants, belonging to the different vaguely distin-
guished regions, but prefer to describe some twenty-eight spots
in various parts of the islands, following entirely the locally col-
lected notes.
Curasao.
The Riff.
This extends near Willemstad on the West side along the
coast and consists of coral-lime with calcareous sand. It con-
tains a number of ruderal and typical litoral plants along the
sea-coast; the small lagunes are rich in Laguncularia racemosa,
Avicennia nitida and Rhizophora Mangle; Philoxerus vermicularis
occurs there as a herb together with Sesuvium portulacastrum;
also an occasional Cyperacea and Heliotropium curassavicum.
Morinda Royoc as a very low shrub together with Euphorbia
thymifolia occurs frequently on the lime grounds, while Conocar-
pus erecta forms whole complexes; also Gundlachia corymbosa
and Suriana maritima...”
|
|
| 16 |
 |
“...the much more scantily overgrown parts of Curasao. Beurena
succulenta and Acacia tortuosa rise above these shrubs together
with Haematoxylon Brasiletto and Machaonia Ottoms; in places
where the shrubs are less dense we find the soil pretty thickly
covered with Tephrosia cinerea, Heliotropium humile, Sida, Chlons,
Mariscus fuligineus, Hyptis pectinata and- Paspalum glabrum,
while Ipomoea winds through everywhere.
A few Bursera bonairensis and Antirrhoea acutata form again,
together with a, large number of Casearia bonairensis and Hae-
matoxylon Brasiletto, the higher shrubs or stick out with Hippo-...”
|
|
| 17 |
 |
“...Acacia villosa, Acacia
tortuosa, Phyllanthus Euwensii, Croton flavens, Jatropha urens
with its very strong stinging hairs, Capparis cynophallophora,
Crescentia Cujete, Malpighia, Machaonia Ottonis and a few Triplaris
coriacea form the high thicket of shrubs. Similar to this is
The calcareous district near Siberie.
It has mainly the same plants, only the following are conspicuous
by their large numbers: Rhacoma crossopetalum, Coccoloba diver-
sifolia, while in more open parts Heliotropium and a number of
grasses coyer the soil. Croton niveus, Malpighia and especially
many Cephalocereus lanuginosus are- together with Guaiacum
officinale and Condalia Henriquezii the principal plants, while
here Metopium Brownei is already one of the tallest trees.
The lime district near Savonet.
Here the soil is more open in many places, the shrubs are less
high, so that Evolvulus, Heliotropium, Croton glandulosus, Sida,
and especially Sporobolus argutus are conspicuous; as a lower
shrub we see Kramera ixina;...”
|
|
| 18 |
 |
“...typical Croton vegetation with Croton
flavens, Casearia bonairensis, Beureria succulenta, Bursera simaruba,
between which also Schoepfia Schreberi, Bumelia obovata,
Caesalpinia coriaria, many Pithecolobum platylobum and Mal-
pighia, Capparis linearis, Bursera tomentosa, Peltophorum Surin-
gari, Tecoma chrysantha, Guaiacum officinale and some, but not
many, Acacia tortuosa. In many places the shrub vegetation is
little developed and the ground is then covered by herbs and low
shrubs of which a number of ruderal plants attract notice, like:
Physalis, Spigelia anthelmia, Hyptis pectinata, Commelina virginica,
Sida supina, Mitracarpus villosus, Spermacoce tenuior, Turnera
pumilea, Elytraria squamosa, Bouteloua aristidoides, Evolvulus
alsinoides, Stylosanthes hamata, Pectis. Of the Cactaceae Cereus
griseus and Cephalocereus lanuginosus are conspicuous. In the
whole hilly complex of Mirlamar and Jamanota Pithecolobium
platylobum is very prominent, especially in the flowering season,
while also...”
|
|
| 19 |
 |
“...Curasao, Aruba, Bonaire + Margarita 150
Curasao, Aruba, Bonaire 249
Margarita 440
399 590
These numbers diverge considerably from those given by Johnston
(p. 302), namely 400 for Curasao, of which 1Ó0 not on Margarita.
From these numbers and more still from the figures of list p. 138,
appears that the flora of Margarita is numerically very different
from that of the Dutch W. I. Islands.
Margarita is much larger than the Dutch Islands. It is not only
its size, however, which causes the larger number of species but
still more the circumstance that higher mountains occur there,
reaching a height of 800 metres.
Although Johnston says (p. 301) that his flora probably does not
1) J. R. Johnston: Flora of the Islands of Margarita and Coche.
Contributions from the Gray Herbarium of Harvard University. New Series.
No. XXXVII (Printed June 1909)....”
|
|
| 20 |
 |
“...165
contain more than % of the real number of species, yet it seemed
to he desirable to compare this flora more closely with the plants,
mentioned in my Systematical part.
Johnston’s flora has 157 genera, not including Filices, which are
not found on Curasao, Aruba and Bonaire and of these some
70 have no representatives at a higher altitude than 300 metres,
while about 80 genera are only found above 300 metres.
So, if we compare the floras of the four islands we must not
include these genera, occurring above 300 metres.
Overagainst these 70 genera of the lower parts which were found
by Johnston and not by me, we have also some 70 which are
found on Curasao, Aruba and Bonaire but not on Margarita.
While the flora of Margarita mainly differs from that of the
Dutch -Leeward Islands by the occurrence of a peculiar flora in
the higher parts, it appears that of the 36 wild indigenous Antil-
les plants which are also found on Margarita, only 8 occur in
the Dutch Islands. So we have
Dutch Leeward...”
|
|
|
